René Wagner
Pitney Bowes - Tier 3/Comet Server VB6 to C# .NET Core Modernization on AWS
TSRI adapted its industry-leading modernization capabilities to the unique Pitney Bowes Visual Basic 6 (VB6) code constructs for a successful automatic modernization of over 443,000 lines of VB6 code and over 450,000 lines of XML meta-data to modern C# .NET Core coming in well within budget and completing the transformation earlier than scheduled.
Additionally, TSRI’s partner, Accenture, had the opportunity to manually rewrite the user interfaces for the application, to achieve a modern and user-friendly experience, while TSRI simultaneously completed the automated transformation of the application code and database written in VB6. As a result, the application achieved total functional equivalence while the look and feel of the front end was greatly improved.
 |
|
- VB6
- C#
- Automatic Refactoring
- VB6 Modernization
- architecture
- Software Modernization
- modernization
- transformation blueprint
- Microsoft SQL Server
- JANUS Studio®
- Code Warranty
- SonarQube
- Functional Equivalence
- Containerized on AWS
- C# NET Core
- Refactoring
- Data Migration
- Database Modernization
- Code Documentation
- automated refactoring
- Automated Modernization
- Cloud Native
Oracle CloudWorld: September 18-21

The TSRI team is excited to be a Showcase Sponsor at this year’s Oracle CloudWorld from September 18th through 21st in Las Vegas, Nevada. Join us for a demo session of our automated modernization process, and a fascinating featured session with other industry leaders.
At CloudWorld, you’ll discover the insights you need for success on your most complex software modernization projects and cloud deployment challenges. The conference will be full of opportunities to meet and learn from industry leaders and technology experts to discover what’s new and what’s next for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure when it comes to databases, applications, and much, much more.
SEPTEMBER 20th SESSION
See 99.9X% Automation in Action
Get a look at how TSRI modernizes a mainframe application modernization from COBOL to Java running on Oracle Cloud at the Modernize Mainframe Applications to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure with Confidence session on Wednesday, September 20th at 2:10pm PDT. Scott Pickett, VP of Product Development and Service Delivery, will demonstrate how it’s done with 99.9X% automation. You'll see how TSRI transforms COBOL, CICS, CA IDEAL, JCL, Pl/1, PL/SQL, and more, to functionally equivalent Java and C# .Net Core with migration to cloud, cloud-hybrid, or modern on-premises environments.
FEATURED SESSION ON SEPTEMBER 21st
Modernizing Mainframe Workloads to OCI
Find out how TSRI clients have achieved 80-90% TCO savings on mainframe modernization. Join Oracle and TSRI on Thursday, September 21st at 9:05 am PDT for a Featured Session on Mainframe Modernization with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. René Wagner and a panel of Oracle partners will share strategies and patterns for modernizing and refactoring mainframe applications to modern environements, including hybrid and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). You’ll learn options and strategies that can cut costs and mitigate risks associated with mainframe migration to the cloud.
Reserve a Personal Genius Bar Session
To receive a more personalized walkthrough, check out our demo session, Cloud for Mission-Critical: Mainframe Offload. Register on the Oracle Events App to join René Wagner at the Genius Bar in the Hub on Wednesday, September 20th from 5-6pm. While you can walk up to the Genius Bar during the session, spots are limited to four attendees at one time per session, so we recommend that you pre-register in advance to avoid missing out.
Stop by Booth #48
Any time during the conference, the TSRI team will be ready and eager to share industry knowledge, successful modernization strategies, and opportunities for partnership. We look forward to seeing you in person at Booth #48 to ensure that every software modernization is done professionally, with full accuracy, assured functional equivalence, and in a fraction of the time.
Meet Us at the Conference!
SCHEDULE NOW

In a fraction of the time, lower cost, and with no business interruption, TSRI’s JANUS Studio® automates the transformation and refactoring of software applications to cloud environments. Our industry-leading reputation for success includes mission-critical mainframe applications for military, government, and private sector organizations.
---
Proven by decades of results. Prove it for yourself.
For decades, TSRI clients have been discovering a dramatically faster, more accurate, and less expensive automated modernization process. We’ve earned a place as the go-to resource for enterprise corporations, government, military, healthcare, and more. Now prove it for yourself. Find out how the proprietary TSRI modernization process delivers future-ready, cloud-based code in any modern language in a fraction of the time.
See Case Studies
Learn About Our Technology
Get Started on Your Modernization Journey Today!
- mainframe
- documentation
- migration
- modernizationjourney
- technology
- whymodernize
- revolution
- software
- modernization
- Microservices
- cloud
- cloudcomputing
- devops
- continuousmodernization
- mainframetocloud
- mainframemodernization
- cloudmodernization
- productivity
- it
- automation
- automatedmodernization
- oraclecloudworld2023
- oraclecloudworld
- oracle
Highlights From MITS 2023

AN AIR FORCE FOCUS ON AUTOMATION
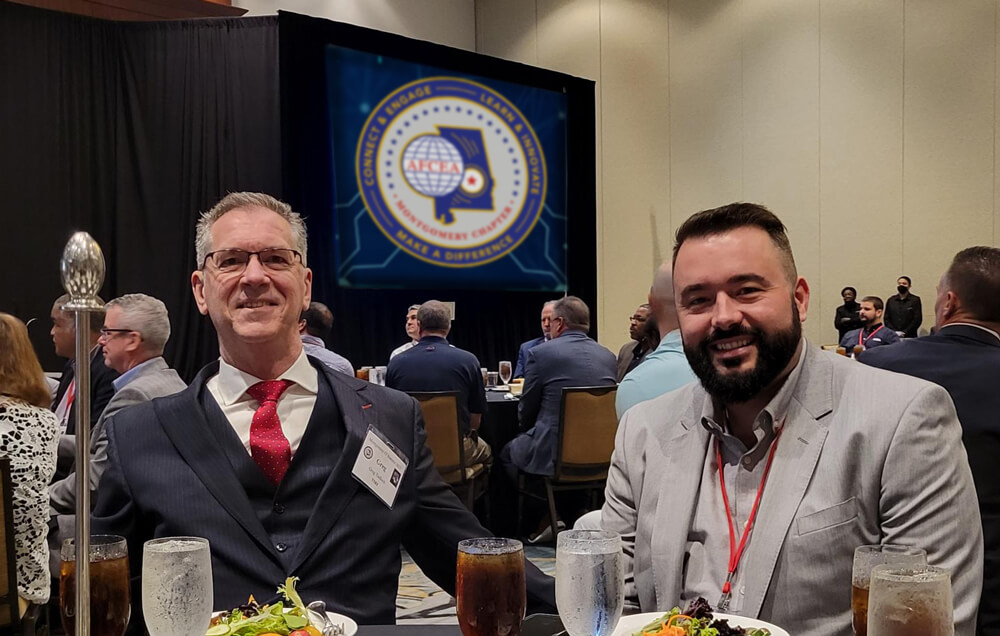
Face to Face with Our Air Force Counterparts
This year’s AFCEA MITS conference in Montgomery, Alabama, was a fantastic experience. The TSRI team was delighted to spend quality time with this community of long-time partners, the U.S. Air Force, and other military leaders. It gave us an in-person opportunity to deepen established relationships and help strengthen our understanding of the Air Force’s critical goals and initiatives. The panel sessions and discussions reflected the impressive intelligence, passion, and dedication of the Air Force and our industry colleagues.
This year we were proud to sponsor the conference to help advance the military’s mission and the education of the future technology workforce through AFCEA’s yearly charity golf tournament and President’s Breakfast.
Conversations on the Green
The golf tournament and breakfast held the day before the conference offered an excellent opportunity to build new relationships and strengthen existing ones in a fun setting. René Wagner, our Director of Business Development, says, “It was very exciting to talk with our partners about how they're feeling about the industry and about our common goal of helping the Air Force.”
Our sponsorship helped AFCEA raise over $127,000 for schools and universities through the Montgomery AFCEA Chapter Education Foundation. The money will go to promote IT integration in classrooms across Alabama’s River Region by providing students and teachers with scholarships, grants, equipment, and awards to support technical workforce development.

Insights from the Main Event
With around 700 attendees, the 2023 MITS conference provided a focused forum for in-depth discussions with the Air Force about their critical IT goals. This year’s conference theme was the “Unwavering Drive for Automation,” a natural fit for TSRI’s automated architecture-driven software application modernization and refactoring solution. Our approach consistently achieves over 99.9% automation, meeting and exceeding Air Force typical expectations of 60% or 70% automation, at minimum. In addition to the time and money TSRI’s high automation solution can save organizations, our iterative refactoring process improves code quality and increases applications' speed, security, readability, and scalability.
Throughout the conference, we heard new ideas for business, mission, and IT automation, and we shared how, at TSRI, we leverage automation at every step of the software modernization journey. In conversations with our partners and USAF customers about the continued success of TSRI’s application modernization solution and process, we gained valuable insight into what sets our approach apart. Beyond our technical solution, these conversations highlighted the importance of our comprehensive planning, diligent expectation setting, and expertise in post-modernization operational change management.
“I’ve been living and breathing the Air Force logistics modernization strategy and struggle for over a decade.” Says Greg Tadlock, TSRI’s Vice President of Sales, “At MITS, what I learned was continued reinforcement that we're on the right track. That what we're offering customers is the right solution.“
Taking Center Stage
“The single greatest moment at the event, for me,” says Greg, “was the full auditorium as René introduced TSRI at the beginning of the automation panel. You can only imagine…for a small company like TSRI, it felt like a big moment.” The panel discussion addressed some of the central questions of automation, such as which business and technical processes make sense to automate and what level of automation is feasible to run critical operations more efficiently for the Air Force and other military organizations. The panel discussed familiar and innovative automation tools and methodologies, including new AI technologies.

Hot Topics: Platform Selection and Cyber-Resilience
In addition to automation and AI, another major topic of conversation was cloud infrastructure and platform migration for military systems. To achieve the high levels of security, performance, and maintainability required of military IT solutions, our Air Force customers need to identify and configure the optimal environments for their systems. Paul Saladna, an Enterprise Architect at NTT Data, responsible for the Air Force’s large and very successful SBSS ILS-S project, speaks to this question in our recent webinar. Do you go with a particular cloud platform based on your systems language or database type? Or do you choose by the server or operating system? In many cases, it’s not a simple, formulaic decision.
As more Air Force and other military systems are migrated to the cloud, several considerations exist in the choice and configuration of their target environments. Cyber-resilience is near the top of the list, as is scalability and the ease of system maintenance. There’s not one “if-System-A-then-Target-B” answer, which made our conversations at MITS all the more interesting and informative. With the Air Force tackling several new initiatives, now is the perfect time to engage in these critical discussions. TSRI consults with our partners and customers to help select cloud environments and configure optimal architectures for each application.
START YOUR MODERNIZATION JOURNEY WITH A TSRI CONSULTATION.
Many thanks to the Air Force and AFCEA for another great MITS!
Greg summed up our feelings about the MITS event: "It was an honor to participate with such an influential group of folks at the Air Force. It was great to get a chance to understand their needs and truly introduce TSRI’s full capabilities.” We look forward to next year and the rewarding initiatives and breakthroughs we’ll tackle with our partners and military colleagues until then!

---
Proven by decades of results. Prove it for yourself.
For decades, TSRI clients have been discovering a dramatically faster, more accurate, and less expensive automated modernization process. We’ve earned a place as the go-to resource for enterprise corporations, government, military, healthcare, and more. Now prove it for yourself. Find out how the proprietary TSRI modernization process delivers future-ready, cloud-based code in any modern language in a fraction of the time.
See Case Studies
Learn About Our Technology
Get Started on Your Modernization Journey Today!
- mainframe
- documentation
- migration
- modernizationjourney
- technology
- whymodernize
- revolution
- software
- modernization
- Microservices
- cloud
- cloudcomputing
- devops
- continuousmodernization
- mainframetocloud
- mainframemodernization
- it
- MITS
- afcea
- AirForce
- automation
- dotheimpossible
- MITSgolf
- automatedmodernization
- productivity
- infrastructure
- MITS2023
- cloudmodernization
- usaf
Let's Meet at MITS!
TEEING OFF FOR AUTOMATION AT THIS YEAR'S AFCEA EVENT IN MONTGOMERY
“Unwavering Drive For Automation.” That’s the theme for this year’s AFCEA MITS (Armed Forces Communications and Electronics Association, Montgomery Information Technology Summit.) And we couldn’t agree more.
It’s no wonder TSRI is a Platinum Sponsor of MITS this year; we’re always innovating to enable greater automation. So if you’re attending MITS, we would love a chance to get together. And don’t miss our Automation Panel Discussion on May 24 moderated by Matt Roberts, AFLCMC/GB DAFBOT. We’ll also be at the Industry/Government Exchange Breakfast Reception on Monday morning. Look for us at either place if you’re going.
To further support our commitment to innovation through teamwork with the Air Force, TSRI is proud to be a MITS Golf Sponsor this year. If you’re going to the tournament, let’s meet up on the fairway. Just drop Greg Tadlock or René Wagner a line and we can coordinate a face-to-face meeting.
ON THE FAIRWAY OR IN THE CONFERENCE ROOMS.
Let's Meet at MITS.
TSRI Automation Panel Discussion
May 24, 08:50 – 09:50 CT
TSRI Golf Sponsorship
Contact Greg Tadlock or René Wagner to connect on the fairway.
On a Mission to Automation
Our long-standing relationship with the US Air Force began in 1995 with the Defense and Finance Accounting Services (DFAS) contract management system, MOCAS, and in our 10 Air Force projects since we’ve consistently aligned our efforts to support their vision of a force “Powered by Airmen, Fueled by Innovation,” modernizing some of the Air Force’s most mission critical systems.
From our modernization of the challenging Air Force AFLCMC SBSS ILS-S—known as “The Beast”— to our current work modernizing the 4-million line Stock Control System, with our partner Definitive Logic, we’ve consistently delivered success. Some of our successful past projects modernizing Air Force systems include:
— Weather monitoring—Weather Data Analysis Capability (WDAC)
— Tactical and strategic multiservice satellite management—MILSTAR (Military Strategic & Tactical Relay
— Reporting systems for equipment maintenance data—The Reliability & Maintainability Information System (REMIS)
— Tracking combat capability and impending parts problems—Weapon System Management Information System (WSMIS),
— Financial cost tracking—WSCRS Weapons System Cost Retrieval System
Let's Touch Base
If you’re going to be at the MITS conference, let’s meet at the session, on the greens, or in-between! Drop us a line at iThis email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. and let’s set up a time to talk about transforming the impossible into the everyday.
---
Proven by decades of results. Prove it for yourself.
For decades, TSRI clients have been discovering a dramatically faster, more accurate, and less expensive automated modernization process. We’ve earned a place as the go-to resource for enterprise corporations, government, military, healthcare, and more. Now prove it for yourself. Find out how the proprietary TSRI modernization process delivers future-ready, cloud-based code in any modern language in a fraction of the time.
See Case Studies
Learn About Our Technology
Get Started on Your Modernization Journey Today!
- mainframe
- documentation
- migration
- modernizationjourney
- technology
- whymodernize
- revolution
- software
- modernization
- Microservices
- cloud
- cloudcomputing
- devops
- continuousmodernization
- mainframetocloud
- mainframemodernization
- awscloud
- cloudmodernization
- infrastructure
- productivity
- it
- MITS
- afcea
- AirForce
- automation
- dotheimpossible
- MITSgolf
- automatedmodernization
Advancing Modernization
DEFINING AND ADVANCING THE FUTURE OF MODERNIZATION
The TSRI team is dedicated to removing the barriers to innovation. We are constantly talking with experts across a broad range of industries, from military to private enterprises to cloud providers, about what modernization means to their organizations, what is coming next in the field, and how they can take advantage of this technology.
In this post, we summarize three topics we hear consistently from customers and partners: the meaning(s) of “modernization”; the motivation to modernize; and how the process has become a movement.
1. What We Mean When We Say "Modernization"

We find people have varying understandings of the phrase “software modernization” depending on their position, needs, and priorities. Options under this umbrella term include line-by-line code conversion, rehosting to a cloud environment, and manual code and architecture refactoring. Really any form of digital transformation, manual or automated, that moves workloads off the mainframe. The Gartner IT Glossary defines Application Modernization Services even more broadly:
“Application modernization services address the migration of legacy to new applications or platforms, including the integration of new functionality to provide the latest functions to the business. Modernization options include replatforming, rehosting, recoding, rearchitecting, reengineering, interoperability, replacement and retirement, as well as changes to the application architecture to clarify which option should be selected.”
Regardless of the terminology, most long-standing organizations understand that it is critical to modernize applications in order to remain competitive. With this rapidly evolving and increasingly necessary industry, it can be a challenge for decision-makers to find and understand their options. At TSRI, our modernization approach simply includes all of it, code, database, architecture, and UI, even CI/CD protocol, while also refactoring for improved quality and performance. And we automate the process at every step of the way for higher rates of accuracy and efficiency; modernizing 100% of the code, the database, and user interfaces from source to target at 99.9X% automation. TSRI’s automated transformation and refactoring uses a unique iterative methodology to not only translate source code into modern languages, but also to improve the quality of the code and optimize the architectures for a modern computing environment in the cloud (or whatever location is right for your application, including on-prem, hybrid, and embedded environments). Our process results in improved application maintainability, readability and performance while reducing security vulnerabilities and technical debt. With automated and intelligent processes, TSRI saves customers time, money, and resources by achieving measurable improvements in weeks instead of months, or years.
Read about our modernization process
2. Top-Down Drivers of Modernization

Look into most Fortune 500 companies and you will find mission-critical applications in need of modernization, 70% according to AWS. Many executives and CEOs are pursuing strategic modernization plans for their organizations over the next few years. Additionally, among the hundreds of technical stakeholders the TSRI team has engaged with in recent months, many director level IT professionals have been instructed by their organization's leadership to begin prioritizing modernization initiatives, if they are not already. It is clear that application modernization is not something that is going to happen in the future — it is necessary now.
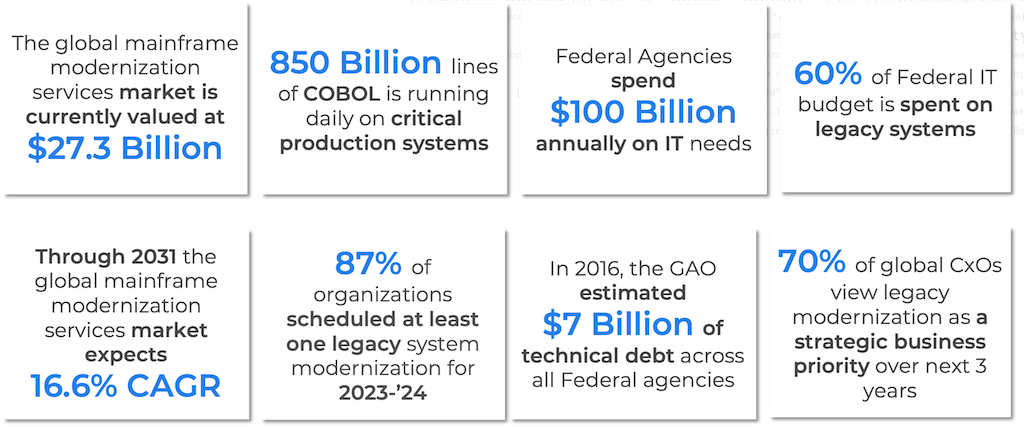
Many of our customers are surprised to hear TSRI has been using an automated process to modernize applications for over 28 years already, and that level of experience means our approach is time-tested for success. While we were a pioneer in the field of automated code modernization, mainframe languages have been around well over 65 years, and were designed for a pre-internet world. Now, after 3 decades, the internet has changed the face of every industry, ushering in many changes in how we all do business. As our business models and technologies develop, continuous modernization will be an essential part of ongoing strategic planning for our critical systems, to both utilize modern technologies and identify and avoid liabilities. With the advent of cloud computing in the past decade, modernization now also enables long-standing organizations to take advantage of cloud agility, cost benefits, and scalability.
3. How Code Modernization is Hitting the Mainstream

Despite understanding that modernization is a beneficial and necessary endeavor, many companies and organizations—even those with highly sophisticated business models and/or national security responsibilities—are still running their applications written in languages developed during the era of mainframes, like COBOL and PL/1. Today, the level of security and performance in the cloud is finally on par with the well-established capabilities of mainframes, and the advent of cloud computing offers increased operational efficiencies and future technology readiness, along with providing access to new tools and services that enable discovery and remediation of security vulnerabilities not uncovered before. The movement towards modernization and cloud migration may also help organizations avoid costly operational issues, such as those recently faced by the airline industry, where technical debt resulted in business disruption and unfavorable national news coverage.
Some organizations are understandably still hesitant to begin a modernization project, because their systems are relied upon daily to keep critical operations moving and a major modernization project can sound daunting, with concerns of costly downtime, low ROI, and even introducing new risk to mission-critical systems. Thankfully, through TSRI’s highly accurate and automated architecture-driven modernization solution, these companies can overcome technical debt and capitalize on new technological opportunities with low risk and no business disruption. TSRI's model- and rule-driven software modernization solution is very cost-effective, delivering a high ROI while still producing the highest quality application transformations, routinely meeting and exceeding the code quality, security, and performance standards of many safety-critical industries, including Dept. of Defense, Banking and Finance, and Healthcare.
Read about TSRI’s modernization services
We’d love to hear your modernization stories, definitions and questions. Get in touch with us now to keep the modernization conversation going.
---
Proven by Decades of Results. Prove It for Yourself.
For decades, TSRI clients have been discovering a dramatically faster, more accurate, and cost-effective automated modernization process. We have earned a place as the go-to resource for enterprise corporations, government, military, healthcare, and more. Now prove it for yourself. Find out how the proprietary TSRI modernization process delivers future-ready, cloud-based code in any modern language in a fraction of the time.
See Case Studies
Learn About Our Technology
Get Started on Your Modernization Journey Today!
- Accenture. (n.d.). Mainframe Migration. Accenture. https://www.accenture.com/us-en/blogs/cloud-computing/mainframe-migration
- CIO. (2021, August 16). Moving beyond legacy: The C-suite guide to application modernisation. Be Ready. https://be-ready.cio.com/collection/application-modernisation/article/moving-beyond-legacy-the-c-suite-guide-to-application-modernisation
- Tata Consultancy Services. (2022, January 18). Mainframe and Legacy Modernisation Top Priority - TCS Survey. Tata World. https://www.tataworld.com/news/openinside/mainframe-and-legacy-modernisation-top-priority-tcs-survey
- Transparency Market Research. (2022, February 9). Mainframe Modernization Services Market to Expand at CAGR of 16.6%: Rising Need for Modernizing Technology Infrastructure to Boost Global Market, Notes TMR. PR Newswire. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/mainframe-modernization-services-market-to-expand-at-cagr-of-16-6-rising-need-for-modernizing-technology-infrastructure-to-boost-global-market-notes-tmr-301421602.html
- Parrish, T. (2022, February 10). COBOL wants to find out just how popular it really is. TechRadar. https://www.techradar.com/news/cobol-wants-to-find-out-just-how-popular-it-really-is
- Simon, A. (2022, December 12). Shifting left on day one. FCW. https://fcw.com/comment/2022/12/shifting-left-day-one/380823/
- Clark, S. (2022, March 31). Senate HSGAC Approves Legacy IT Reduction Act, Blocks Funding. MeriTalk. https://www.meritalk.com/articles/senate-hsgac-approves-legacy-it-reduction-act-blocks-funding/
- Manyika, J., Chui, M., Miremadi, M., Bughin, J., George, K., Willmott, P., & Dewhurst, M. (2020, May 14). How COVID-19 has pushed companies over the technology tipping point—and transformed business forever. McKinsey & Company. https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/strategy-and-corporate-finance/our-insights/how-covid-19-has-pushed-companies-over-the-technology-tipping-point-and-transformed-business-forever
- Konkel, F. (2022, March 31). New bill would mandate legacy IT inventories, modernization plans. Federal News Network. https://federalnewsnetwork.com/congress/2022/03/new-bill-would-mandate-legacy-it-inventories-modernization-plans/
Educational Testing Service (ETS) - IBM COBOL to Java SE 17 Modernization on AWS
Educational Testing Service (ETS) is the world's largest private educational testing and measurement organization. Each year, they develop, administer, and score more than 50 million tests, including the TOEFL®, TOEIC®, GRE®, and Praxis® tests, in more than 180 countries. This requires an enormous data management capability. ETS turned to TSRI to transform their ECT and Praxis applications and databases from IBM job control language (JCL) and COBOL Batch to modern Java SE 17 in a cloud-native optimized AWS environment. To do this, they used a spring boot-type application to implement web services invoked by Python. TSRI also converted the IBM DB2 database and VSAM sequential database files to a relational PostgreSQL database on AWS Aurora.
 |
Customer: Educational Testing Service (ETS) Source & Target Language: IBM COBOL to Java SE 17 on AWS Lines of Code: 1,199,633 lines of COBOL and JCL Duration: 11 Months Services: Automated Code Transformation, Automated Refactoring, Integration and Testing Support, SonarQube Quality Refactoring, Code-Specific Adaptation, Database Migration, Transformation "To-Be" Blueprint®, Application "As-Is" Blueprint®, Code Warranty
|
- sql
- transformation blueprint
- Platform Migration
- modernization
- Software Code Modernization
- Refactoring
- Code Documentation
- modernize
- migration
- Data
- Data Migration
- assessment
- architecture
- multitier
- Microservices
- Micro Services
- monolithic
- Security Refactoring
- application modernization
- System Modernization
- Object Oriented
- Quality Output
- Asis Blueprint
- Software Modernization
- Modern Architecture
- ArchitectureDriven
- Software Transformation
- transformation
- cloudnative
- containerized
- modularized
- cobol
- mainframe
- COBOL to Java
- Java
- db2
- DB2 Database
- VSAM
- Monolithic COBOL
- COBOL Modernization
- COBOL Conversion
- Business Case
- DB/2 and VSAM
- stepwise
- input/output (DIO) layer
- SonarQube
- Quality Standards
- SonarQube Quality
- IBM z/OS
- IBM z/OS COBOL
- COBOL and CICS
- cics
- VSAM sequential files to relational
- VSAM to relational database
- PostgreSQL
- PostgreSQL on AWS Aurora
- user interface
- BMS
- BMS to Angular
- BMS to Web Screens
- Containerized on AWS
- Cost Savings
- Green Screen Modernization
- Architecture Diagram
- BMS to CSS
- BMS to HTML5
- Monolithic to Multitier
- Monolithic to cloud native
- VSAM to modern database
- jcl
- batch
AWS re:Invent 2022: Stack the Cloud Modernization Odds in Your Favor
Going to AWS re:Invent 2022 in Las Vegas? The TSRI team is. The magic number to remember for accelerating and assuring your software modernization projects is 846. That’s our booth at the event where you’ll find our team and hear about our advanced JANUS Studio® solution to modernize your software applications to the AWS cloud.

DON'T GAMBLE WITH SOLUTIONS WHEN IT COMES TO YOUR CODE.
CONNECT WITH THE EXPERTS AT TSRI.
AWS Mainframe Migration Competency Partners
As a vetted and validated AWS Mainframe Migration Competency partner, TSRI provides rapid, low-risk software modernization for deployment on AWS.
Stop by to see how the TSRI team has strategically planned and executed hundreds of successful modernization projects. We’ll be ready to discuss the business and technical details of our modernization solution and answer questions about how TSRI transforms more than 35 different languages operating without code-freeze and business disruption in a graceful, step-wise manner.

GAIN A FAST ADVANTAGE
AWS ISV Accelerate Program Member
At the booth, you can get a head-start on launching projects from kick-off and execution to ongoing operations on the AWS cloud. Because TSRI has earned membership in the AWS ISV Accelerate Program, we offer prioritized access to the AWS co-sell support team to drive faster adoption of ISV solutions. That means our customers get access to valuable resources that provide guidance to achieve better results through collaboration with the powerful AWS Sales and Account Management organizations.
YOU'VE GOT QUESTIONS
We've got over 250 successful migrations to reference
We speak from experience. TSRI has transformed some of the most secure and mission-critical military, government, and finance systems in the world to full business operations in cloud-ready modern languages. Our team at AWS re:Invent would love to share insights from real-world case studies across a broad range of industries.
— Ask us how we saved Pitney Bowes 97% on their annual Total Cost of Ownership by moving them—without disruption—from COBOL on an HP NonStop Tandem mainframe to a modern C# .NET Core application in production on AWS.
— You might also want to know how it only took six weeks to move the Canada Revenue Agency’s Help Desk application to AWS—while reducing their annual system maintenance costs by 80%.
— While you’re there, find out how we achieved a 99.9996% automation rate in modernizing all but one or two lines of code while transforming Educational Testing Services (ETS) from COBOL and JCL to Java and Python on AWS. That included a high-transaction batch system, DB2 and VSAM to PostgreSQL, as well as a very large number and variety of sort cards that required automation. We would love to tell you how we did it—and show you what we can do for you!

STOP BY BOOTH #846 OR PRE-SCHEDULE YOUR VISIT NOW
We love talking about this stuff. That’s partly why we love AWS re:Invent so much. It’s our chance to meet you face-to-face.
Our team of experts will be available to answer questions about your specific application modernization scenario, provide demonstrations, and share case studies of TSRI’s successful modernization projects spanning government, military, finance, insurance, retail, and many other industries. To get expert one-on-one modernization advice at AWS re:Invent put yourself on our calendar now.
Schedule a Session
---
Proven by Decades of Results. Prove It for Yourself.
For decades, TSRI clients have been discovering a dramatically faster, more accurate, and less expensive AI-based and automated modernization process. We’ve earned a place as the go-to resource for enterprise corporations, government, military, healthcare, and more. Now prove it for yourself. Find out how the proprietary TSRI modernization process delivers future-ready, cloud-based code in any modern language in a fraction of the time.
See Case Studies
Learn About Our Technology
Get Started on Your Modernization Journey Today!
Budget Surplus Is a Dirty Word

In stark contrast to its 2021 numbers, the US Federal Government expects to end this fiscal year (2022) with a surplus of $308 billion dollars according to the Congressional Budget Office. (As opposed to last year’s $226 billion deficit.) While that excess fuels clickable headlines for politicians, it’s not great news if your agency or department uses less budget than you predicted—while possibly falling short of longer term goals such as software modernization.
“Use it, or lose it” is a real thing that has caused Federal Government agencies and departments to lose or cut over $127 billion between 2009 and 2019. In one stark example from 2019, the Department of Defense had to return $80 billion in unused budget.
![]()
The average amount of budget fund cancelation is about 1.6% annually.”
According to the Government Accountability Office, the average amount of budget fund cancelation is about 1.6% annually. While that number doesn’t sound large, it can have an erosive effect on your budget and create a downward trend that can be more difficult to reverse down the road when increases could be genuinely needed. And while the examples above are government figures, the principle is the same in the private sector—or even more tightly policed.
So, what can you do as we near the end of your fiscal year if you find yourself with that ugly surplus—even of a measly one or two percent or less? We’ve got four suggestions for you:
1. NOTCH YOUR ARROWS FOR NEXT YEAR
Take some time to cast ahead to your fiscal 2023 strategy. What updates and improvements would you like to see by the end of next year?

Knowing that you have money in your coffers ahead of time, consider what additional resources, technology, or assistance will help you achieve those goals. Are there moderate investments such as modernization planning that you can make this year that could give you wiggle room should the vagaries of budget and crisis change your situation next year? Are there plans you’d like to lock in now?
As you envision what next year should look like, consider software modernization. One smart use of funds ahead of a modernization project is using the final couple of months of this year to get an assessment for your program. It only took TSRI six weeks to assess the entire AT&T billing system with 961,780 lines of code and comments through our JANUS Studio®, delivering an Application Blueprint® that enabled them to begin the next phases of their modernization more efficiently.
![]()
It only took TSRI six weeks to assess the entire AT&T billing system with 961,780 lines of code.”
2. UPSKILL YOUR TEAM
Professional development does more than grow your organizational toolkit of capabilities; it also helps employee retention during a time of 3.5% unemployment.

In a fascinating 2022 learning and development study, LinkedIn found that the #1 driver of workplace culture (and so, retention) is opportunities to learn and grow. And in a time where languages like COBOL and Ada don’t even rank in the top ten searched languages, training in modern languages can also pay off for your organization. In a Microsoft-sponsored study, IDC found that IT professionals who have achieved a relevant role-based technical certification perform on average 26% better than their uncertified colleagues with the same responsibilities. Certifying your people is worth the investment.
3. UPGRADE YOUR TECHNOLOGY
If you have money left over, it’s a great time to provide your teams with technology that matches both the needs of a more mobile, more connected, and more secure world.

These can be affordable, pointed investments that can pay off with increased productivity, security, and employee satisfaction while positioning your teams to face changing needs. As you consider your options, think in terms of:
Mobility: More powerful and secure laptops and tablets
Business processes: Point of sale for retail, connected medical devices
Cloud computing: New as-a-Service applications, storage devices, and subscriptions
Cybersecurity: Assess and upgrade your current measures
Automation: Software, AI, and services to automate large, repetitive, or formerly impossible tasks
Let’s talk about that last one.
4. GET A FIRM HANDLE ON YOUR CURRENT CODE
Even if you’re not planning on modernizing code, poorly written or undocumented applications that are written in hard-to-understand languages can be a huge IT operating expense for you.

A Harris poll found that developers spend an average of 17 hours a week (42% of their time) dealing with bad code. Basic understanding of code content should be a prerequisite for any software-managing organization: know what’s there. But with millions, or tens of millions of lines of code, that can be very difficult or impossible to do manually.
![]()
Developers spend an average of 17 hours a week (42% of their time) dealing with bad code.”
That’s where TSRI DocsRev makes a powerful investment in all 365 days of 2023—and beyond.
DocsRev is automated code documentation-as-a-Service. It allows users with varying experience levels to quickly familiarize themselves with the structure and flow of the application through easily navigable diagrams, hyperlinking code, and other UML artifacts and graphics. It’s powered by the same automated tools our clients have trusted to document the world’s most critical applications since 1995. Now our technology is available to you as a simply-priced and easy-to-manage service that keeps you up to date on what’s really in your code.
In addition to giving you always-current code documentation, DocsRev apprises you on your application's current complexity, structure, control flow, data flow, similarity, and dead code. All you need to do is upload your latest code baseline to receive complete and detailed documentation.
Trusted by major organizations around the world for application maintenance and development, DocsRev frees you from uncertainty by letting you easily inspect and identify external calls, utilities, and interfaces. DocsRev shows you what your code is actually up to by automatically exposing EXEC statements your application is using such as SQL, CICS, and more.
Let’s Make Your 2023 Budget Process Go Smoothly
Throughout next year and beyond, your code will change based on your needs. To make sure you have the right views into whatever happens in your code, the DocsRev team is continually adding new views, graphs, indices, diagrams, and other features to its documentation set.
---
Proven by Decades of Results. Prove It for Yourself.
For decades, TSRI clients have been discovering a dramatically faster, more accurate, and less expensive AI-based and automated modernization process. We’ve earned a place as the go-to resource for enterprise corporations, government, military, healthcare, and more. Now prove it for yourself. Find out how the proprietary TSRI modernization process delivers future-ready, cloud-based code in any modern language in a fraction of the time.
See Case Studies
Learn About Our Technology
Get Started on Your Modernization Journey Today!
- mainframe
- documentation
- migration
- modernizationjourney
- technology
- whymodernize
- productivity
- it
- infrastructure
- revolution
- software
- modernization
- Microservices
- cloud
- cloudcomputing
- devops
- continuousmodernization
- mainframetocloud
- mainframemodernization
- docsrev
- codedocumentation
- 2022budgetsurplus
- excessbudget
Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) Help Desk - COBOL to Java Modernization on AWS
CRA and AWS engaged with TSRI to complete the modernization of their COBOL-based system to Java on AWS. To Achieve CRA's goals, TSRI tuned JANUS Studio® to parse, transform, document, and refactor the IBM z/OS COBOL application. In just 1.5 months, TSRI modernized the application from an IBM Mainframe COBOL and CICS monolith to a modern multi-tier architecture in Java on the AWS cloud. Just as important, TSRI also converted the DB2 database and VSAM sequential files to a relational PostgreSQL database on AWS Aurora.
 |
Customer: Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) and AWS Source & Target Language: IBM COBOL to Java on AWS Lines of Code: 168,000 Duration: 1.5 Months Services: Automated Code Transformation, Automated Refactoring, Integration and Testing Support, SonarQube Quality Refactoring, Code-Specific Adaptation, Database Migration, Transformation "To-Be" Blueprint®, Application "As-Is" Blueprint®
|
- sql
- transformation blueprint
- Platform Migration
- modernization
- Software Code Modernization
- Refactoring
- Code Documentation
- modernize
- migration
- Data
- Data Migration
- assessment
- architecture
- multitier
- Microservices
- Micro Services
- monolithic
- Security Refactoring
- application modernization
- System Modernization
- Object Oriented
- Quality Output
- Asis Blueprint
- Software Modernization
- Modern Architecture
- ArchitectureDriven
- Software Transformation
- transformation
- cloudnative
- containerized
- modularized
- cobol
- mainframe
- COBOL to Java
- Java
- db2
- DB2 Database
- VSAM
- Monolithic COBOL
- COBOL Modernization
- COBOL Conversion
- Business Case
- DB/2 and VSAM
- stepwise
- input/output (DIO) layer
- SonarQube
- Quality Standards
- SonarQube Quality
- IBM z/OS
- IBM z/OS COBOL
- COBOL and CICS
- cics
- VSAM sequential files to relational
- VSAM to relational database
- PostgreSQL
- PostgreSQL on AWS Aurora
- user interface
- BMS
- BMS to Angular
- BMS to Web Screens
- Containerized on AWS
- Cost Savings
- Green Screen Modernization
- Architecture Diagram
- BMS to CSS
- BMS to HTML5
- Monolithic to Multitier
- Monolithic to cloud native
- VSAM to modern database
- jcl
- batch
Pitney Bowes Postage Payment System Modernization HP Tandem COBOL to C# on AWS
The Pitney Bowes Postage Payment Application had been running COBOL for decades on an HP NonStop Tandem mainframe, however, to seize the opportunities of the digital cloud age and to reduce overall technical debt, Pitney Bowes needed to modernize the Tandem COBOL to C# .NET Core. Just as important as the code, the HP NonStop Tandem database needed to also be migrated to a modern Microsoft SQL Server database and deployed to AWS. TSRI successfully transformed the application at 99.96% automation, and deployed the modernized application on the AWS cloud.
 |
Customer: Pitney Bowes Inc. Source & Target Language: COBOL to C# .Net Core on AWS Lines of Code: 390,000 Duration: 6 Months Services: Automated Code Transformation (99.96% level of automation), Automated Refactoring, Database Conversion: File based system to a Microsoft SQL Environment, Integration and Testing Support, Transformation Blueprint®, Application "As-Is" Blueprint®,
|
- sql
- transformation blueprint
- Platform Migration
- modernization
- Software Code Modernization
- Refactoring
- Code Documentation
- modernize
- migration
- Data
- Data Migration
- assessment
- architecture
- multitier
- Microservices
- Micro Services
- monolithic
- Security Refactoring
- application modernization
- System Modernization
- Object Oriented
- Quality Output
- Asis Blueprint
- Software Modernization
- Modern Architecture
- ArchitectureDriven
- Software Transformation
- transformation
- cloudnative
- containerized
- modularized
- State Contract
- RFI
- RFP
- cobol
- COBOL to C#
- VAX COBOL
- RMS flat file
- database
- Open VMS RMS Flat Files
- to SQL
- to SQL Server environment
- Architecture Driven
- Cloud based
- MS SQL Server
- Microsoft SQL
- COBOL to C# NET Core
- NET Core
- AWS Cloud
- HP NonStop Tandem Mainframe
- mainframe modernization
- Mainframe Migration
- HP Tandem
- HP Nonstop
- Postal System Migration
- Postal System Modernization
- Cost Savings
- Mainframe cost saving
- Cost of ownership
- From Monolithic to multitier
- distributed architecture

